In the world of logistics, transport, and shipping, the theory of von Thunen’s Belts has stood the test of time as a foundational principle that continues to influence how goods are moved from place to place. This theory, developed by German economist Johann Heinrich von Thunen in the early 19th century, offers valuable insights into the organization of transportation networks and the spatial distribution of economic activities. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of von Thunen’s Belts and explore its enduring relevance in the modern era of global trade and commerce.
Understanding von Thunen’s Belt Theory in Logistics
Von Thunen’s Belt Theory is a fundamental concept in logistics that helps explain the spatial organization of economic activities in relation to transportation costs. According to this theory, different types of goods are produced in concentric rings around a central market, with the intensity of land use decreasing as distance from the market increases. This has significant implications for transportation and shipping logistics, as it highlights the importance of proximity to markets in reducing transportation costs.
By understanding von Thunen’s Belt Theory, logistics professionals can optimize supply chain efficiency and resource allocation. This knowledge can help in determining the most cost-effective transportation routes, warehousing locations, and distribution strategies. Additionally, it can aid in forecasting demand patterns and planning inventory levels to meet customer needs. Overall, von Thunen’s Belt Theory provides a valuable framework for analyzing and improving logistics operations in a complex and interconnected global economy.

Strategies for Implementing Transport Efficiency in von Thunen’s Belts
Implementing transport efficiency in von Thunen’s belts is crucial for optimizing logistics and shipping in agricultural regions. One strategy is to establish centralized distribution centers within each belt to streamline transportation and reduce overall costs. These hubs can act as consolidation points for goods before being shipped out to markets, increasing efficiency and reducing the number of trips needed.
Another key strategy is to invest in modern transportation infrastructure such as highways, railways, and waterways to improve connectivity between von Thunen’s belts and urban markets. By utilizing multiple modes of transportation, goods can be transported more efficiently, reducing delivery times and transportation costs. Additionally, implementing sustainable practices such as using electric vehicles and optimizing route planning can further enhance transport efficiency in von Thunen’s belts.

Maximizing Shipping Effectiveness within von Thunen’s Agricultural Zones
Von Thunen’s Agricultural Zones offer a unique framework for understanding the relationship between land use and transportation logistics. By strategically locating industries and agricultural activities based on proximity to market centers, shipping effectiveness can be maximized within each zone. This concept allows for efficient distribution of goods and services, reducing transportation costs and increasing overall productivity.
Implementing von Thunen’s theory within modern supply chain management involves careful planning and coordination of transportation routes, modes, and infrastructure. Leveraging technologies such as GPS tracking, real-time data analytics, and automated warehousing systems can further enhance the efficiency of shipping operations within each zone. By optimizing the use of available resources and minimizing transportation distances, businesses can achieve cost savings and competitive advantages in the market.
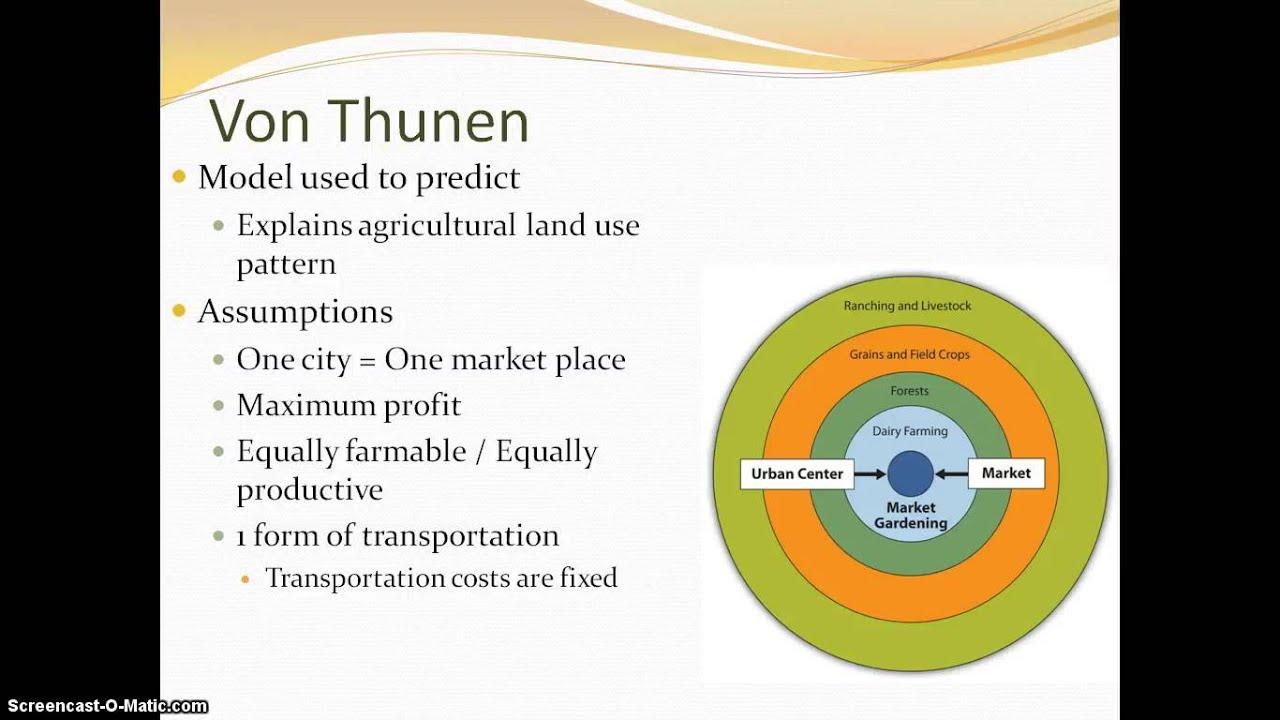
Utilizing von Thunen’s Model to Optimize Supply Chain Management
can provide valuable insights into the spatial organization of production and distribution. By understanding the principles of land use and transportation costs outlined in the model, businesses can strategically plan their logistics, transport, and shipping operations to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. This approach allows companies to create a more streamlined and sustainable supply chain network, ultimately leading to improved profitability and customer satisfaction.
By implementing von Thunen’s belts concept, businesses can categorize their suppliers, warehouses, and distribution centers based on their proximity to the market. This segmentation allows companies to prioritize transportation modes and routes, optimize inventory levels, and reduce lead times. Additionally, applying this model to supply chain management can help identify opportunities for collaboration and consolidation with other partners within the same belt, further enhancing operational efficiency and cost effectiveness.
In Summary
In conclusion, von Thunen’s Belts provide a valuable framework for understanding the spatial organization of logistics, transport, and shipping operations. By considering the economic principles of land use and transportation costs, businesses can optimize their supply chain strategies and make informed decisions about location and infrastructure investments. As technology continues to advance and global markets become increasingly interconnected, the principles of von Thunen’s Belts remain relevant in the ever-evolving landscape of logistics. By applying these principles to real-world scenarios, businesses can navigate the complex web of supply chain dynamics and stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing world.
